Business Writing Truths and Myths

Written by Lynn Gaertner-Johnston, Syntax Training
For the 25 years I have taught classes in business writing, I have heard and rejected a few myths. And I have learned and applied some important truths. Don’t let yourself be fooled by false rules that others may follow. Recognize and apply what makes sense.
Is each of the five statements below a truth, a myth, or a mix of both depending on the situation? You decide. Read More…
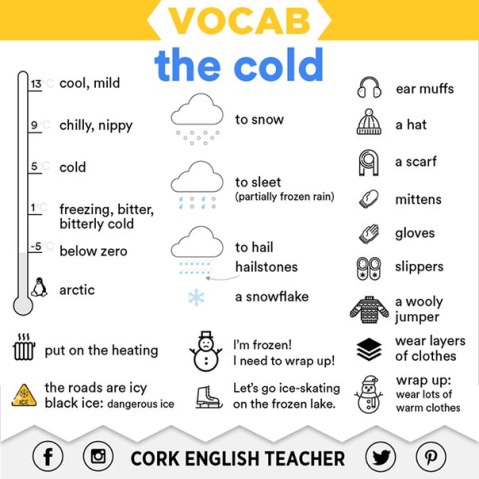
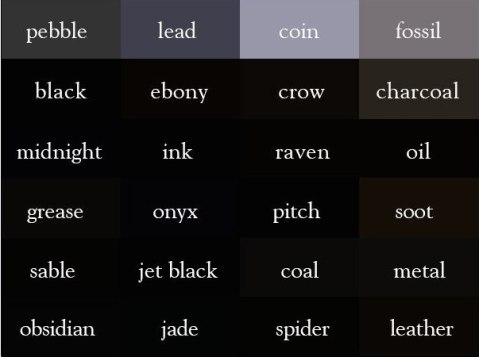
240 color names in English
From snow to jade, if you are struggling to describe a color or you just want to broaden your vocabulary.
(Although the blacks seem all the same to me.)








No more boring sentences
I don’t know if it’s just me, but it seems like we, as writers, do get so wrapped up in the actions, thoughts and relationships of our characters that we completely forget to dress it up. Sentences get so long-winded in action and thought that any descriptive narrative is just left in the dust. With this tutorial, we will remedy that. Hopefully.
You may ask: What am I to do? And I shall tell you: You just need to start small, using basic descriptive words and work up to more complicated and sophisticated sentence structures.
- Let’s start with a plain, basic sentence.
Ollie sat underneath the tree.
- Let’s replace Ollie with a pronoun and give the tree a species.
A boy sat underneath the willow tree.
- Ask yourself this. How old is the boy? Is he very young? Or is he more of a teen? Is the tree dying? Is it a young tree? Use words like “young” or “lively” to give your character (or any other living things in the scene) an age group and a starting point to visualizing your character for the reader. We’re just going to call the boy “young” for right now.
A young boy sat underneath the willow tree.
- Now we need some sort of action the boy (or the tree) could be doing. just sitting isn’t going to cut it. when adding more action to a sentence, it would range anywhere from a single word to an entire phrase. just make sure that when you add the action that it moves with the rest of the sentence in a coherent fashion and that there is proper punctuation to accommodate it. for our little example sentence, we’re going to add a phrase.
A young boy sat underneath the willow tree, watching a breeze.
- “Watching the breeze” sounded all nice and fluffy when we first put it, but after we’ve read it a few times it sounds sort sort of ridiculous. One can’t literally watch a breeze, right? Here we can just add an action for the breeze to be doing simultaneously with the action of the boy. The boy doesn’t even have to have any awareness of what the breeze is doing at all. So, we will just change a few words around and add something for the breeze to do.
A young boy sat underneath the willow tree, as a breeze flitted through the bulrushes.
- Now that you are starting to get the hand of this, we can just skip a bunch of the steps and get to the end part, where we have a lovely and descriptive sentence worthy of opening your post. Below, as you can see, we added a few more choice words, replaced some things and moved some phrases around.
As a gentle breeze flitted through the bulrushes, a young boy sat contemplating underneath the ancient willow tree.
How to write much better
or not.
1. Avoid alliteration. Always.
2. Prepositions are not to end sentence with.
3. Avoid clichès like the plague (They’re old hat.).
4. Eschew ampersands & abbreviations, etc.
5. One should never generalize.
6. Comparisons are as bad as clichès.
7. Be more or less specific.
8. Sentence fragments. Eliminate.
9. Exaggeration is a billion times worse than understatement.
10. Parenthetical remarks (however relevant) are unnecessary.
11. Who needs rhetorical questions?
The Politically Incorrect Etymologies of 10 Words and Phrases
At various moments in its life, a word will hop languages, change meanings, travel through sinister moments and land in pleasant ones. But no matter how many times it’s superimposed, and how far it gets from its original source, a word doesn’t let go of its memories easily. Here are 11 modern English words with socially insensitive origins.
1. Hysteria (n.) – a wild, irrational eruption of fear or emotion
Hysteria begins in the womb, or so thought the medical scholars of the 1610s, who named the condition after the Latin hystericus, meaning “of the womb.” Those who’ve studied the Victorian era, or read The Awakening in high school, may know that the go-to prognosis of the time for just about every female’s symptom from the occasional hissy fit to chronic seizures was a pesky wayfaring uterus. The condition was thought to be caused by sexual frustration and cured by intercourse or pelvic massage, the latter often performed by physicians and midwives. When doctors finally got fed up with the tedious task in the late 19th century, the personal vibrator was created to take their place. Read More…
14 Words That Are Their Own Opposites

Here’s an ambiguous sentence for you: “Because of the agency’s oversight, the corporation’s behavior was sanctioned.” Does that mean, ‘Because the agency oversaw the company’s behavior, they imposed a penalty for some transgression‘ or does it mean, ‘Because the agency was inattentive, they overlooked the misbehavior and gave it their approval by default’? We’ve stumbled into the looking-glass world of “contronyms”—words that are their own antonyms.
1. Sanction (via French, from Latin sanctio(n-), from sancire ‘ratify,’) can mean ‘give official permission or approval for (an action)’ or conversely, ‘impose a penalty on.’
*
2. Oversight is the noun form of two verbs with contrary meanings, “oversee” and “overlook.” “Oversee,” from Old English ofersēon ‘look at from above,’ means ‘supervise’ (medieval Latin for the same thing: super- ‘over’ + videre ‘to see.’) “Overlook” usually means the opposite: ‘to fail to see or observe; to pass over without noticing; to disregard, ignore.’
*
3. Left can mean either remaining or departed. If the gentlemen have withdrawn to the drawing room for after-dinner cigars, who’s left? (The gentlemen have left and the ladies are left.)
*
4. Dust, along with the next two words, is a noun turned into a verb meaning either to add or to remove the thing in question. Only the context will tell you which it is. When you dust are you applying dust or removing it? It depends whether you’re dusting the crops or the furniture.
*
5. Seed can also go either way. If you seed the lawn you add seeds, but if you seed a tomato you remove them.
*
6. Stone is another verb to use with caution. You can stone some peaches, but please don’t stone your neighbor (even if he says he likes to get stoned).
*
7. Trim as a verb predates the noun, but it can also mean either adding or taking away. Arising from an Old English word meaning ‘to make firm or strong; to settle, arrange,’ “trim” came to mean ‘to prepare, make ready.’ Depending on who or what was being readied, it could mean either of two contradictory things: ‘to decorate something with ribbons, laces, or the like to give it a finished appearance’ or ‘to cut off the outgrowths or irregularities of.’ And the context doesn’t always make it clear. If you’re trimming the tree are you using tinsel or a chain saw?
*
8. Cleave can be cleaved into two “homographs,” words with different origins that end up spelled the same. “Cleave,” meaning ‘to cling to or adhere,’ comes from an Old English word that took the forms cleofian, clifian, or clīfan. “Cleave,” with the contrary meaning ‘to split or sever (something), ‘ as you might do with a cleaver, comes from a different Old English word, clēofan. The past participle has taken various forms: “cloven,” which survives in the phrase “cloven hoof,” “cleft,” as in a “cleft palate” or “cleaved.”
*
9. Resign works as a contronym in writing. This time we have homographs, but not homophones. “Resign,” meaning ‘to quit,’ is spelled the same as “resign,” meaning ‘to sign up again,’ but it’s pronounced differently.
*
10. Fast can mean “moving rapidly,” as in “running fast,” or ‘fixed, unmoving,’ as in “holding fast.” If colors are fast they will not run. The meaning ‘firm, steadfast’ came first. The adverb took on the sense ‘strongly, vigorously,’ which evolved into ‘quickly,’ a meaning that spread to the adjective.
*
11. Off means ‘deactivated,’ as in “to turn off,” but also ‘activated,’ as in “The alarm went off.”
*
12. Weather can mean ‘to withstand or come safely through,’ as in “The company weathered the recession,” or it can mean ‘to be worn away’: “The rock was weathered.”
*
13. Screen can mean ‘to show’ (a movie) or ‘to hide’ (an unsightly view).
*
14. Help means ‘assist,’ unless you can’t help doing something, when it means ‘prevent.’
Read more: Contronyms: What did you mean by ‘deceptievly’ smart?